radis.io package¶
Submodules¶
- radis.io.cache_files module
- radis.io.cdsd module
- radis.io.dbmanager module
- radis.io.exomol module
- radis.io.exomol_utils module
- radis.io.exomolapi module
- radis.io.geisa module
- radis.io.hdf5 module
- radis.io.hitemp module
- radis.io.hitran module
- radis.io.npy module
- radis.io.query module
- radis.io.spec_hdf module
- radis.io.tools module
Module contents¶
Parsers for various databases
- cdsd2df(fname, version='hitemp', cache=True, load_columns=None, verbose=True, drop_non_numeric=True, load_wavenum_min=None, load_wavenum_max=None, engine='pytables')[source]¶
Convert a CDSD-HITEMP [1]_ or CDSD-4000 [2]_ file to a Pandas dataframe.
- Parameters
fname (str) – CDSD file name
version (str (‘4000’, ‘hitemp’)) – CDSD version
cache (boolean, or ‘regen’) – if
True, a pandas-readable HDF5 file is generated on first access, and later used. This saves on the datatype cast and conversion and improves performances a lot (but changes in the database are not taken into account). IfFalse, no database is used. If ‘regen’, temp file are reconstructed. DefaultTrue.load_columns (list) – columns to load. If
None, loads everythingNote
this is only relevant if loading from a cache file. To generate the cache file, all columns are loaded anyway.
- Other Parameters
drop_non_numeric (boolean) – if
True, non numeric columns are dropped. This improves performances, but make sure all the columns you need are converted to numeric formats before hand. DefaultTrue. Note that if a cache file is loaded it will be left untouched.load_wavenum_min, load_wavenum_max (float) – if not
'None', only load the cached file if it contains data for wavenumbers above/below the specified value. See :py:func`~radis.io.cache_files.load_h5_cache_file`. Default'None'.engine (‘pytables’, ‘vaex’) – format for Hdf5 cache file. Default
pytables
- Returns
df – dataframe containing all lines and parameters
- Return type
pandas Dataframe
Notes
CDSD-4000 Database can be downloaded from 3
Performances: I had huge performance trouble with this function, because the files are huge (500k lines) and the format is to special (no space between numbers…) to apply optimized methods such as pandas’s. A line by line reading isn’t so bad, using struct to parse each line. However, we waste typing determining what every line is. I ended up using the fromfiles functions from numpy, not considering n (line return) as a special character anymore, and a second call to numpy to cast the correct format. That ended up being twice as fast.
initial: 20s / loop
with mmap: worse
w/o readline().rstrip(’n’): still 20s
numpy fromfiles: 17s
no more readline, 2x fromfile 9s
Think about using cache mode too:
no cache mode 9s
cache mode, first time 22s
cache mode, then 2s
Moving to HDF5:
On cdsd_02069_02070 (56 Mb)
Reading:
cdsd2df(): 9.29 s cdsd2df(cache=True [old .txt version]): 2.3s cdsd2df(cache=True [new h5 version, table]): 910ms cdsd2df(cache=True [new h5 version, fixed]): 125ms
Storage:
%timeit df.to_hdf("cdsd_02069_02070.h5", "df", format="fixed") 337ms %timeit df.to_hdf("cdsd_02069_02070.h5", "df", format="table") 1.03s
References
Note that CDSD-HITEMP is used as the line database for CO2 in HITEMP 2010
See also
- fetch_astroquery(molecule, isotope, wmin, wmax, verbose=True, cache=True, expected_metadata={}, engine='pytables-fixed')[source]¶
Download a HITRAN line database to a Pandas DataFrame.
Wrapper to the fetch function of Astroquery [1]_ (itself based on [HAPI])
Note
if using, cite [HAPI] and [HITRAN-2020]
- Parameters
molecule (str, or int) – molecule name or identifier
isotope (int) – isotope number
wmin, wmax (float (cm-1)) – wavenumber min and max
- Other Parameters
verbose (boolean) – Default
Truecache (boolean or
'regen') – ifTrue, tries to find a.h5cache file in the Astroquerycache_location, that would match the requirements. If not found, downloads it and saves the line dataframe as a.h5file in the Astroquery. If'regen', delete existing cache file to regerenate it.expected_metadata (dict) – if
cache=True, check that the metadata in the cache file correspond to these attributes. Argumentsmolecule,isotope,wmin,wmaxare already added by default.
References
See also
astroquery.hitran.core.Hitran.query_lines_async(),astroquery.query.BaseQuery.cache_location
- fetch_exomol(molecule, database=None, local_databases=None, databank_name='EXOMOL-{molecule}', isotope='1', load_wavenum_min=None, load_wavenum_max=None, columns=None, cache=True, verbose=True, clean_cache_files=True, return_local_path=False, return_partition_function=False, engine='default', output='pandas', skip_optional_data=True)[source]¶
Stream ExoMol file from EXOMOL website. Unzip and build a HDF5 file directly.
Returns a Pandas DataFrame containing all lines.
- Parameters
molecule (
str) – ExoMol moleculedatabase (
str) – database name. Ex::POKAZATELorBT2forH2O. SeeKNOWN_EXOMOL_DATABASE_NAMES. IfNoneand there is only one database available, use it.local_databases (
str) – where to create the RADIS HDF5 files. Default"~/.radisdb/exomol". Can be changed inradis.config["DEFAULT_DOWNLOAD_PATH"]or in ~/radis.json config filedatabank_name (
str) – name of the databank in RADIS Configuration file Default"EXOMOL-{molecule}"isotope (
strorint) – load only certain isotopes, sorted by terrestrial abundances :'1','2', etc. Default1.Note
In RADIS, isotope abundance is included in the line intensity calculation. However, the terrestrial abundances used may not be relevant to non-terrestrial applications. By default, the abundance is given reading HITRAN data. If the molecule does not exist in the HITRAN database, the abundance is read from the
radis/radis_default.jsonconfiguration file, which can be modified by editingradis.configafter import or directly by editing the user~/radis.jsonuser configuration file (overwritesradis_default.json). In theradis/radis_default.jsonfile, values were calculated with a simple model based on the terrestrial isotopic abundance of each element.load_wavenum_min, load_wavenum_max (float (cm-1)) – load only specific wavenumbers.
columns (list of str) – list of columns to load. If
None, returns all columns in the file.
- Other Parameters
cache (bool, or
'regen'or'force') – ifTrue, use existing HDF5 file. IfFalseor'regen', rebuild it. If'force', crash if not cache file found. DefaultTrue.verbose (bool)
clean_cache_files (bool) – if
Trueclean downloaded cache files after HDF5 are created.return_local_path (bool) – if
True, also returns the path of the local database file.return_partition_function (bool) – if
True, also returns aPartFuncExoMolobject.engine (‘vaex’, ‘feather’) – which memory-mapping library to use. If ‘default’ use the value from ~/radis.json
output (‘pandas’, ‘vaex’, ‘jax’) – format of the output DataFrame. If
'jax', returns a dictionary of jax arrays. If'vaex', output is avaex.dataframe.DataFrameLocalNote
Vaex DataFrames are memory-mapped. They do not take any space in RAM and are extremelly useful to deal with the largest databases.
skip_optional_data (bool) – If False, fetch all fields which are marked as available in the ExoMol definition file. If True, load only the first 4 columns of the states file (“i”, “E”, “g”, “J”). The structure of the columns above 5 depend on the the definitions file (*.def) and the Exomol version. If
skip_optional_data=False, two errors may occur:a field is marked as present/absent in the *.def field but is absent/present in the *.states file (ie both files are inconsistent).
in the updated version of Exomol, new fields have been added in the states file of some species. But it has not been done for all species, so both structures exist. For instance, the states file of https://exomol.com/data/molecules/HCl/1H-35Cl/HITRAN-HCl/ follows the structure described in [1]_, unlike the states file of https://exomol.com/data/molecules/NO/14N-16O/XABC/ which follows the structure described in [2]_.
- Returns
df (pd.DataFrame) – Line list A HDF5 file is also created in
local_databasesand referenced in the RADIS config file with namedatabank_namelocal_path (str) – path of local database file if
return_local_path
Examples
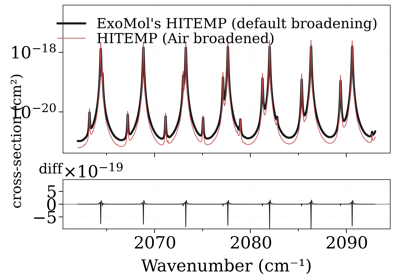
Compare CO xsections from the ExoMol and HITEMP database
Compare CO xsections from the ExoMol and HITEMP databaseNotes
if using
load_only_wavenum_above/beloworisotope, the whole database is anyway downloaded and uncompressed tolocal_databasesfast access .HDF5 files (which will take a long time on first call). Only the expected wavenumber range & isotopes are returned. The .HFD5 parsing useshdf2df()References
- 1
Tennyson, J., Yurchenko, S. N., Al-Refaie, A. F., Barton, E. J., Chubb, K. L., Coles, P. A., … Zak, E. (2016). The ExoMol database: molecular line lists for exoplanet and other hot atmospheres. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jms.2016.05.002
- 2
Tennyson, J., Yurchenko, S. N., Al-Refaie, A. F., Clark, V. H. J., Chubb, K. L., Conway, E. K., … Yurchenko, O. P. (2020). The 2020 release of the ExoMol database: Molecular line lists for exoplanet and other hot atmospheres. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 255, 107228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2020.107228
See also
- fetch_geisa(molecule, local_databases=None, databank_name='GEISA-{molecule}', isotope=None, load_wavenum_min=None, load_wavenum_max=None, columns=None, cache=True, verbose=True, chunksize=100000, clean_cache_files=True, return_local_path=False, engine='default', output='pandas', parallel=True)[source]¶
Stream GEISA file from GEISA website. Unzip and build a HDF5 file directly.
Returns a Pandas DataFrame containing all lines.
- Parameters
molecule (all 58 GEISA 2020 molecules. See here https://geisa.aeris-data.fr/interactive-access/?db=2020&info=ftp)
local_databases (str) – where to create the RADIS HDF5 files. Default
"~/.radisdb/geisa". Can be changed inradis.config["DEFAULT_DOWNLOAD_PATH"]or in ~/radis.json config filedatabank_name (str) – name of the databank in RADIS Configuration file Default
"GEISA-{molecule}"isotope (str, int or None) – load only certain isotopes :
'2','1,2', etc. IfNone, loads everything. DefaultNone.load_wavenum_min, load_wavenum_max (float (cm-1)) – load only specific wavenumbers.
columns (list of str) – list of columns to load. If
None, returns all columns in the file.
- Other Parameters
cache (
True,False,'regen'or'force') – ifTrue, use existing HDF5 file. IfFalseor'regen', rebuild it. If'force', raise an error if cache file cannot be used (useful for debugging). DefaultTrue.verbose (bool)
chunksize (int) – number of lines to process at a same time. Higher is usually faster but can create Memory problems and keep the user uninformed of the progress.
clean_cache_files (bool) – if
Trueclean downloaded cache files after HDF5 are created.return_local_path (bool) – if
True, also returns the path of the local database file.engine (‘pytables’, ‘vaex’, ‘default’) – which HDF5 library to use to parse local files. If ‘default’ use the value from ~/radis.json
output (‘pandas’, ‘vaex’, ‘jax’) – format of the output DataFrame. If
'jax', returns a dictionary of jax arrays. If'vaex', output is avaex.dataframe.DataFrameLocalNote
Vaex DataFrames are memory-mapped. They do not take any space in RAM and are extremelly useful to deal with the largest databases.
parallel (bool) – if
True, uses joblib.parallel to load database with multiple processes
- Returns
df (pd.DataFrame) – Line list A HDF5 file is also created in
local_databasesand referenced in the RADIS config file with namedatabank_namelocal_path (str) – path of local database file if
return_local_path
Examples
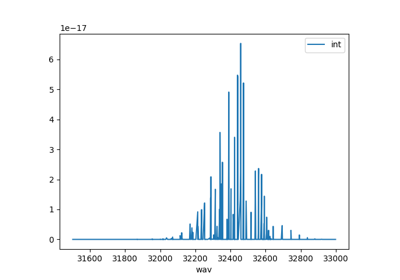
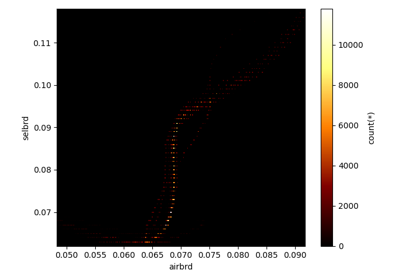
from radis import fetch_geisa df = fetch_geisa("CO") print(df.columns) >>> Index(['wav', 'int', 'airbrd', 'El', 'globu', 'globl', 'locu', 'locl', 'Tdpgair', 'isoG', 'mol', 'idG', 'id', 'iso', 'A', 'selbrd', 'Pshft', 'Tdpair', 'ierrA', 'ierrB', 'ierrC', 'ierrF', 'ierrO', 'ierrR', 'ierrN', 'Tdpgself', 'ierrS', 'Pshfts', 'ierrT', 'Tdppself', 'ierrU'], dtype='object')
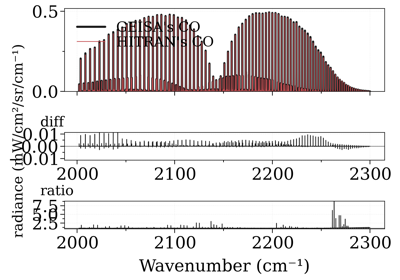
Compare CO spectrum from the GEISA and HITRAN database
Compare CO spectrum from the GEISA and HITRAN databaseNotes
if using
load_only_wavenum_above/beloworisotope, the whole database is anyway downloaded and uncompressed tolocal_databasesfast access .HDF5 files (which will take a long time on first call). Only the expected wavenumber range & isotopes are returned. The .HFD5 parsing useshdf2df()See also
fetch_hitran(),fetch_exomol(),fetch_hitemp(),hdf2df(),fetch_databank()
- fetch_hitemp(molecule, local_databases=None, databank_name='HITEMP-{molecule}', isotope=None, load_wavenum_min=None, load_wavenum_max=None, columns=None, cache=True, verbose=True, chunksize=100000, clean_cache_files=True, return_local_path=False, engine='default', output='pandas', parallel=True)[source]¶
Stream HITEMP file from HITRAN website. Unzip and build a HDF5 file directly.
Returns a Pandas DataFrame containing all lines.
- Parameters
molecule (
"H2O", "CO2", "N2O", "CO", "CH4", "NO", "NO2", "OH") – HITEMP molecule. See https://hitran.org/hitemp/local_databases (str) – where to create the RADIS HDF5 files. Default
"~/.radisdb/hitemp". Can be changed inradis.config["DEFAULT_DOWNLOAD_PATH"]or in ~/radis.json config filedatabank_name (str) – name of the databank in RADIS Configuration file Default
"HITEMP-{molecule}"isotope (str, int or None) – load only certain isotopes :
'2','1,2', etc. IfNone, loads everything. DefaultNone.load_wavenum_min, load_wavenum_max (float (cm-1)) – load only specific wavenumbers.
columns (list of str) – list of columns to load. If
None, returns all columns in the file.
- Other Parameters
cache (
True,False,'regen'or'force') – ifTrue, use existing HDF5 file. IfFalseor'regen', rebuild it. If'force', raise an error if cache file cannot be used (useful for debugging). DefaultTrue.verbose (bool)
chunksize (int) – number of lines to process at a same time. Higher is usually faster but can create Memory problems and keep the user uninformed of the progress.
clean_cache_files (bool) – if
Trueclean downloaded cache files after HDF5 are created.return_local_path (bool) – if
True, also returns the path of the local database file.engine (‘pytables’, ‘vaex’, ‘default’) – which HDF5 library to use to parse local files. If ‘default’ use the value from ~/radis.json
output (‘pandas’, ‘vaex’, ‘jax’) – format of the output DataFrame. If
'jax', returns a dictionary of jax arrays. If'vaex', output is avaex.dataframe.DataFrameLocalNote
Vaex DataFrames are memory-mapped. They do not take any space in RAM and are extremelly useful to deal with the largest databases.
parallel (bool) – if
True, uses joblib.parallel to load database with multiple processes
- Returns
df (pd.DataFrame) – Line list A HDF5 file is also created in
local_databasesand referenced in the RADIS config file with namedatabank_namelocal_path (str) – path of local database file if
return_local_path
Examples
from radis import fetch_hitemp df = fetch_hitemp("CO") print(df.columns) >>> Index(['id', 'iso', 'wav', 'int', 'A', 'airbrd', 'selbrd', 'El', 'Tdpair', 'Pshft', 'ierr', 'iref', 'lmix', 'gp', 'gpp', 'Fu', 'branch', 'jl', 'syml', 'Fl', 'vu', 'vl'], dtype='object')

Compare CO xsections from the ExoMol and HITEMP database
Compare CO xsections from the ExoMol and HITEMP databaseNotes
if using
load_only_wavenum_above/beloworisotope, the whole database is anyway downloaded and uncompressed tolocal_databasesfast access .HDF5 files (which will take a long time on first call). Only the expected wavenumber range & isotopes are returned. The .HFD5 parsing useshdf2df()See also
fetch_hitran(),fetch_exomol(),fetch_geisa(),hdf2df(),fetch_databank()
- fetch_hitran(molecule, extra_params=None, local_databases=None, databank_name='HITRAN-{molecule}', isotope=None, load_wavenum_min=None, load_wavenum_max=None, columns=None, cache=True, verbose=True, clean_cache_files=True, return_local_path=False, engine='default', output='pandas', parallel=True, parse_quanta=True)[source]¶
Download all HITRAN lines from HITRAN website. Unzip and build a HDF5 file directly.
Returns a Pandas DataFrame containing all lines.
- Parameters
molecule (str) – one specific molecule name, listed in HITRAN molecule metadata. See https://hitran.org/docs/molec-meta/ Example: “H2O”, “CO2”, etc.
local_databases (str) – where to create the RADIS HDF5 files. Default
"~/.radisdb/hitran". Can be changed inradis.config["DEFAULT_DOWNLOAD_PATH"]or in ~/radis.json config filedatabank_name (str) – name of the databank in RADIS Configuration file Default
"HITRAN-{molecule}"isotope (str) – load only certain isotopes :
'2','1,2', etc. IfNone, loads everything. DefaultNone.load_wavenum_min, load_wavenum_max (float (cm-1)) – load only specific wavenumbers.
columns (list of str) – list of columns to load. If
None, returns all columns in the file.extra_params (‘all’ or None) – Downloads all additional columns available in the HAPI database for the molecule including parameters like
gamma_co2,n_co2that are required to calculate spectrum in co2 diluent. For eg:from radis.io.hitran import fetch_hitran df = fetch_hitran('CO', extra_params='all', cache='regen') # cache='regen' to regenerate new database with additional columns
- Other Parameters
cache (
True,False,'regen'or'force') – ifTrue, use existing HDF5 file. IfFalseor'regen', rebuild it. If'force', raise an error if cache file cannot be used (useful for debugging). DefaultTrue.verbose (bool)
clean_cache_files (bool) – if
Trueclean downloaded cache files after HDF5 are created.return_local_path (bool) – if
True, also returns the path of the local database file.engine (‘pytables’, ‘vaex’, ‘default’) – which HDF5 library to use. If ‘default’ use the value from ~/radis.json
output (‘pandas’, ‘vaex’, ‘jax’) – format of the output DataFrame. If
'jax', returns a dictionary of jax arrays. If'vaex', output is avaex.dataframe.DataFrameLocalNote
Vaex DataFrames are memory-mapped. They do not take any space in RAM and are extremelly useful to deal with the largest databases.
parallel (bool) – if
True, uses joblib.parallel to load database with multiple processesparse_quanta (bool) – if
True, parse local & global quanta (required to identify lines for non-LTE calculations ; but sometimes lines are not labelled.)
- Returns
df (pd.DataFrame) – Line list A HDF5 file is also created in
local_databasesand referenced in the RADIS config file with namedatabank_namelocal_path (str) – path of local database file if
return_local_path
Examples
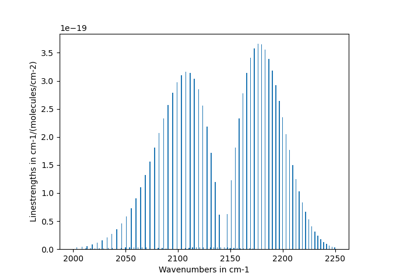
from radis.io.hitran import fetch_hitran df = fetch_hitran("CO") print(df.columns) >>> Index(['id', 'iso', 'wav', 'int', 'A', 'airbrd', 'selbrd', 'El', 'Tdpair', 'Pshft', 'gp', 'gpp', 'branch', 'jl', 'vu', 'vl'], dtype='object')

Compare CO spectrum from the GEISA and HITRAN database
Compare CO spectrum from the GEISA and HITRAN databaseNotes
if using
load_only_wavenum_above/beloworisotope, the whole database is anyway downloaded and uncompressed tolocal_databasesfast access .HDF5 files (which will take a long time on first call). Only the expected wavenumber range & isotopes are returned. The .HFD5 parsing useshdf2df()See also
- hit2df(fname, cache=True, verbose=True, drop_non_numeric=True, load_wavenum_min=None, load_wavenum_max=None, engine='pytables', parse_quanta=True)[source]¶
Convert a HITRAN/HITEMP [1]_ file to a Pandas dataframe
- Parameters
fname (str) – HITRAN-HITEMP file name
cache (boolean, or
'regen'or'force') – ifTrue, a pandas-readable HDF5 file is generated on first access, and later used. This saves on the datatype cast and conversion and improves performances a lot (but changes in the database are not taken into account). If False, no database is used. If'regen', temp file are reconstructed. DefaultTrue.
- Other Parameters
drop_non_numeric (boolean) – if
True, non numeric columns are dropped. This improves performances, but make sure all the columns you need are converted to numeric formats before hand. DefaultTrue. Note that if a cache file is loaded it will be left untouched.load_wavenum_min, load_wavenum_max (float) – if not
'None', only load the cached file if it contains data for wavenumbers above/below the specified value. See :py:func`~radis.io.cache_files.load_h5_cache_file`. Default'None'.engine (‘pytables’, ‘vaex’) – format for Hdf5 cache file. Default
pytablesparse_quanta (bool) – if
True, parse local & global quanta (required to identify lines for non-LTE calculations ; but sometimes lines are not labelled.)
- Returns
df – dataframe containing all lines and parameters
- Return type
pandas Dataframe
References
Notes
Performances: see CDSD-HITEMP parser
See also