radis.io.hitran module¶
RADIS Hitran Functions; based on Common API hitranapi.py
- fetch_hitran(molecule, extra_params=None, local_databases=None, databank_name='HITRAN-{molecule}', isotope=None, load_wavenum_min=None, load_wavenum_max=None, columns=None, cache=True, verbose=True, clean_cache_files=True, return_local_path=False, engine='default', output='pandas', parallel=True, parse_quanta=True)[source]¶
Download all HITRAN lines from HITRAN website. Unzip and build a HDF5 file directly.
Returns a Pandas DataFrame containing all lines.
- Parameters:
molecule (str) – one specific molecule name, listed in HITRAN molecule metadata. See https://hitran.org/docs/molec-meta/ Example: “H2O”, “CO2”, etc.
local_databases (str) – where to create the RADIS HDF5 files. Default
"~/.radisdb/hitran". Can be changed inradis.config["DEFAULT_DOWNLOAD_PATH"]or in ~/radis.json config filedatabank_name (str) – name of the databank in RADIS Configuration file Default
"HITRAN-{molecule}"isotope (str) – load only certain isotopes :
'2','1,2', etc. IfNone, loads everything. DefaultNone.load_wavenum_min, load_wavenum_max (float (cm-1)) – load only specific wavenumbers.
columns (list of str) – list of columns to load. If
None, returns all columns in the file.extra_params (‘all’ or None) – Downloads all additional columns available in the HAPI database for the molecule including parameters like
gamma_co2,n_co2that are required to calculate spectrum in co2 diluent. For eg:from radis.io.hitran import fetch_hitran df = fetch_hitran('CO', extra_params='all', cache='regen') # cache='regen' to regenerate new database with additional columns
- Other Parameters:
cache (
True,False,'regen'or'force') – ifTrue, use existing HDF5 file. IfFalseor'regen', rebuild it. If'force', raise an error if cache file cannot be used (useful for debugging). DefaultTrue.verbose (bool)
clean_cache_files (bool) – if
Trueclean downloaded cache files after HDF5 are created.return_local_path (bool) – if
True, also returns the path of the local database file.engine (‘pytables’, ‘vaex’, ‘default’) – which HDF5 library to use. If ‘default’ use the value from ~/radis.json
output (‘pandas’, ‘vaex’, ‘jax’) – format of the output DataFrame. If
'jax', returns a dictionary of jax arrays. If'vaex', output is avaex.dataframe.DataFrameLocalNote
Vaex DataFrames are memory-mapped. They do not take any space in RAM and are extremely useful to deal with the largest databases.
parallel (bool) – if
True, uses joblib.parallel to load database with multiple processesparse_quanta (bool) – if
True, parse local & global quanta (required to identify lines for non-LTE calculations ; but sometimes lines are not labelled.)
- Returns:
df (pd.DataFrame or vaex.dataframe.DataFrameLocal) – Line list A HDF5 file is also created in
local_databasesand referenced in the RADIS config file with namedatabank_namelocal_path (str) – path of local database file if
return_local_path
Examples
from radis.io.hitran import fetch_hitran df = fetch_hitran("CO") print(df.columns) >>> Index(['id', 'iso', 'wav', 'int', 'A', 'airbrd', 'selbrd', 'El', 'Tdpair', 'Pshft', 'gp', 'gpp', 'branch', 'jl', 'vu', 'vl'], dtype='object')
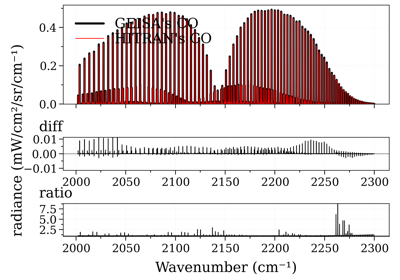
Compare CO spectrum from the GEISA and HITRAN database
Compare CO spectrum from the GEISA and HITRAN databaseNotes
if using
load_only_wavenum_above/beloworisotope, the whole database is anyway downloaded and uncompressed tolocal_databasesfast access .HDF5 files (which will take a long time on first call). Only the expected wavenumber range & isotopes are returned. The .HFD5 parsing useshdf2df()See also
fetch_hitemp(),fetch_exomol(),fetch_geisa(),hdf2df(),fetch_databank()



